Inductive conductivity measurement
Sensors for the inductive measurement of the conductivity of media generate central values for the control of CIP-processes:
- Constant concentration control of the cleaning media in the feed tanks
- Monitoring the concentration during the cleaning phases
- As part of the phase separation to recover the chemicals used
Technologies Details
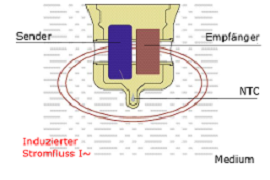
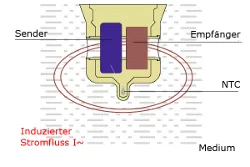
Alternating current flowing through a primary coil (emitter) induces an alternating magnetic field, which in turn induces a current in the surrounding medium. The current flow in the medium on its side produces a magnetic field which induces a tension and consequently a flowing current in the secondary coil (receiver). The current which can be measured is the parameter for the conductivity of the medium. As the conductivity of a liquid depends significantly on the temperature, an additional detector in the sensor tip (NTC) continuously measures the temperature of the medium. The influence of the temperature is compensated by the temperature coefficient value (TC value) preset in the electronic device.



Copyright © 2022 Anderson-Negele